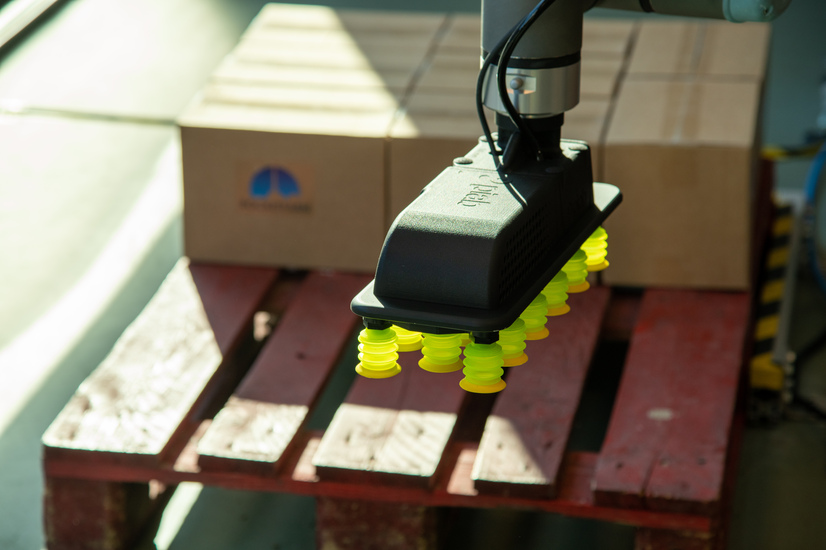
Characteristics of future production
Predictions for tomorrow’s production plants

The competition for today’s production plants have come a long way when it comes to getting up efficiency and in several cases high-tech production facilities.
However, there is a lot of development potential in the area. Especially for SME production facilities, there is a lot of potential for improvement and a lot of manual labor. Some predict that factories will be fully automated in the future. The big question is whether there will also be a room for human resources? This article aims to cast some light on this key question.
The balance between humans and robots
Through an EU project the Danish Institute of Technology has assessed the right balance between humans and machines, and concluded that factories will not be 100 percent fully automated. Even though the robots in the future do much of the work that humans do today and did in the past, there is still a great need for human competence.
Robots complement humans
The reason for this is especially because it is difficult to replace human creativity. There are also huge costs involved in fully automating the production processes. Robots do not replace humans, they complement them by taking over the heavy, tedious and stressful work. This allows humans to place their full attention on doing more creative and meaningful tasks as well as possible. This collaboration contributes to a more effective process and a better product quality. A future where people work with robots and not like robots, as Kim Povlsen CEO at Universal robots has phrased it.

Predictions for tomorrow’s production plants
The human aspect
It is every production engineer’s dream to fully automate human tasks within a factory. The idea of having a robot do all the work, day and night is a tempting dream. For most this dream is broken by the costs of fully automating a factory, a rule of thumb is 80/20, 80 percent automation and 20 percent manual labor. The reason for this is that the cost of automating the last 20 percent is significantly higher than the first 80 percent.
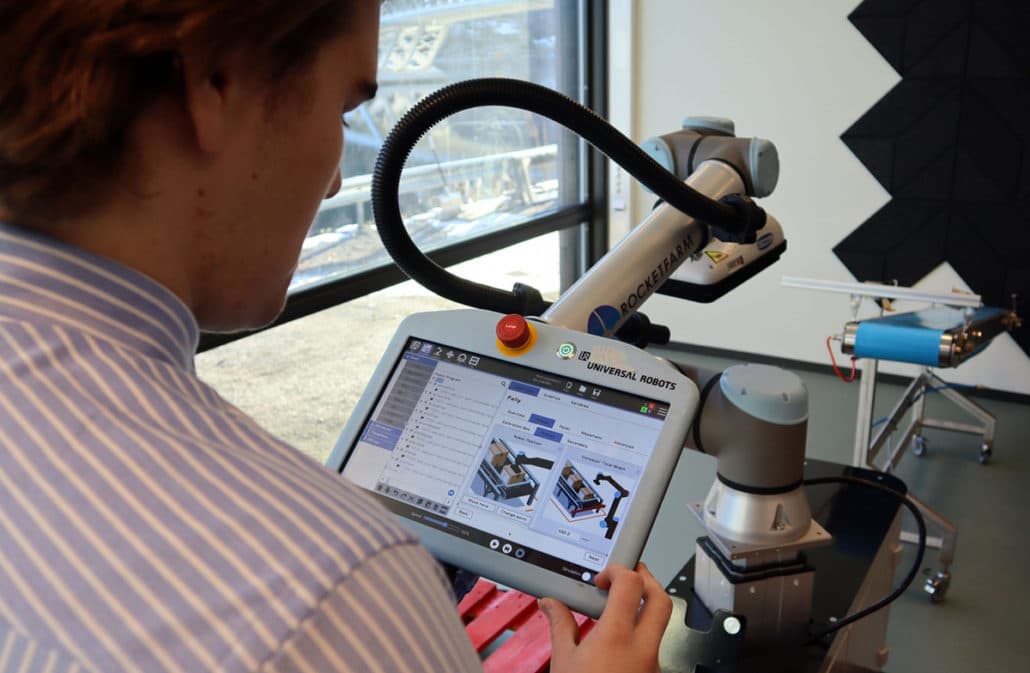
Cobot palletizing – a good example
A solution to this issue could be using robots and cobots for the heavy lifting, repetitive tasks leaving humans to either operate the robot or shift their focus elsewhere on more crucial tasks. Palletizing with collaborative robots is a great example of how to utilize this strategy. Palletizing is the act of placing products on a pallet for shipping og storage, it is a very repetitive and labor intensive task. The task can easily be solved by a cobot with just a few steps, by using a cobot to do this operation you can liberate human resources to do other tasks while keeping or even increasing the production. As the cobot does not require a lot of space or heavy upfront investments it is a great solution for SME`s.
Learn more about how to automate palletizing with collaborative robots here
Reconfigurable production
The current static production lines where many of the same products are produced will probably be replaced by a more customized production where fewer and different products are produced. This requires mobile and collaborative robots that are capable of transporting across the factory. This flexible and customized production is referred to as reconfigurable production.
Demanding customers
This type of production refers to a more customer oriented approach, for small and medium enterprises it could be an issue to deliver such a flexible production setup. Customers will also be more demanding in the form of wanting the product faster and often cheaper. The industry must therefore produce new products ever faster. The ability to restructure production quickly will therefore be absolutely crucial in tomorrow’s market.

Which technology becomes important?
Artificial intelligence will play an important role in the factories of the future. This will help robots to detect quality defects in advanced planning software that can predict machine breakdowns and propose adjustments in production, based on for example, delays or price adjustments on raw materials.
Visualization technologies such as XR technology will be a big part of the future as a tool for gathering information to ease decision making. XR technology can be used in areas where humans can not or should not interfere, this could be anything from dangerous, sterile and hard to reach work environments.

Recycling
Raw material handling and recycling are important topics in the industry, and are something that will stay relevant in the years to come as the world has become more aware of and is starting to reconsider its access to raw material. A sustainable contribution is to buy back the previous products and rebuild it into new solutions, in order for it to work the product design must account for possible re-use to simplify and encourage re-use.
Digital testing
Predictions tells us that businesses will rely more and more on data/automatic solutions when making decisions. This opens up a whole new range of possibilities. As we speak digital twins for different solutions are in use, but not on a massive scale. Digital twins allows you to simulate efficiency and calculate ROI`s with the help of cloud based solutions instead of doing time consuming calculations based on physical experimentation and engineering skills.
With digital twins and increasing trust in technology the process of making a decision is not as complex as it used to be, this could lead to more automation and less manual labor.
Industry 5.0
The fourth industrial revolution left us with a way to maximize profit by lowering costs and increasing production. All of the tools are extremely accessible such as the internet of things, cloud based computing, smart sensors etc. the customers are happy and returning for more because of personalization and absorbing features.
Yet there are questions raised about imbalance between machines and humans. Industry 5.0 addresses these questions and aims to create a symbiotic relationship between humans and robots. To learn more about industry 5.0 follow this link.
The elephant in the room
All of this sounds great, but is the future reserved only for the larger and resourceful organizations? Small and medium sized enterprises in particular are facing challenges in adapting, not just to the predictions above, but also industry 4.0 in general. As have already been recognized in scientific studies. A critical part could be shifting to reconfigurable production, as this could require a major shift in production and financial power. The technological institute has committed to a new project with the EU (SHOP4CF) which addresses this issue. SHOP4CF is short for Smart Human Oriented Platform for Connected Factories, their vision is stated in the following way:
“SHOP4CF aims to find the right balance between cost-effective automation, repetitive tasks and involve the human workers in areas such as adaptability, creativity and agility where they create the biggest added value. Also to pursue the highly-connected factory model to reap the benefits of all the data generated within the factory.”
Even though it is mostly large organizations such as Volkswagen, Siemens and Bosch who are onboard, the targeted audience is small and medium sized enterprises. To achieve this they want to create an open source platform where anyone can access tools to adapt new technology, share knowledge and experience.
The future of SME`s
Industry 4.0(5.0) is coming. We strongly believe that collaborative robots are going to be an integral part of the future due to flexibility, the ability to work next to humans and a big potential within SME`s. Gigafactories and large corporations combining assets has put additional pressure on the SME`s. This makes it hard to gain competitive advantage in a high speed, production oriented market with demanding customers.
To avoid getting wiped out of existence, smaller organizations are now automating their product lines with collaboration robots and working their way towards a symbiotic relationship between humans and robots. Digital testing and upfront validation will play a crucial part in tomorrow’s industry as this allows everyone to test, validate and easily estimate ROI before investing.
With projects like SHOP4CF and tools like digital twins we believe there is room for both gigafactories and small to medium sized factories tomorrow.
Sign up for our newsletter and get a FREE ebook
By signing up for our monthly newsletter, you’ll get case stories, product launches, and tips to automate your production line!
Additionally, you will instantly receive an ebook about implementing palletizing. For more information, please visit our newsletter subscription page.




